
Back in 2005, Federal Reserve Chairman Alan Greenspan described the dramatic increases in residential real estate values as a “froth in housing markets.” Greenspan went on to say:
“The increase in the prevalence of interest-only loans and the introduction of more-exotic forms of adjustable-rate mortgages are developments of particular concern…some households may be employing these instruments to purchase homes that would otherwise be unaffordable, and consequently their use could be adding to pressures in the housing market.”
Greenspan was warning that the loosening of lending standards could lead to disaster. And it did.
With home prices again appreciating at percentages well above historic norms, many are wondering whether the market is again becoming “frothy.” Mortgage standards are much stricter now, however, than they were in 2005.
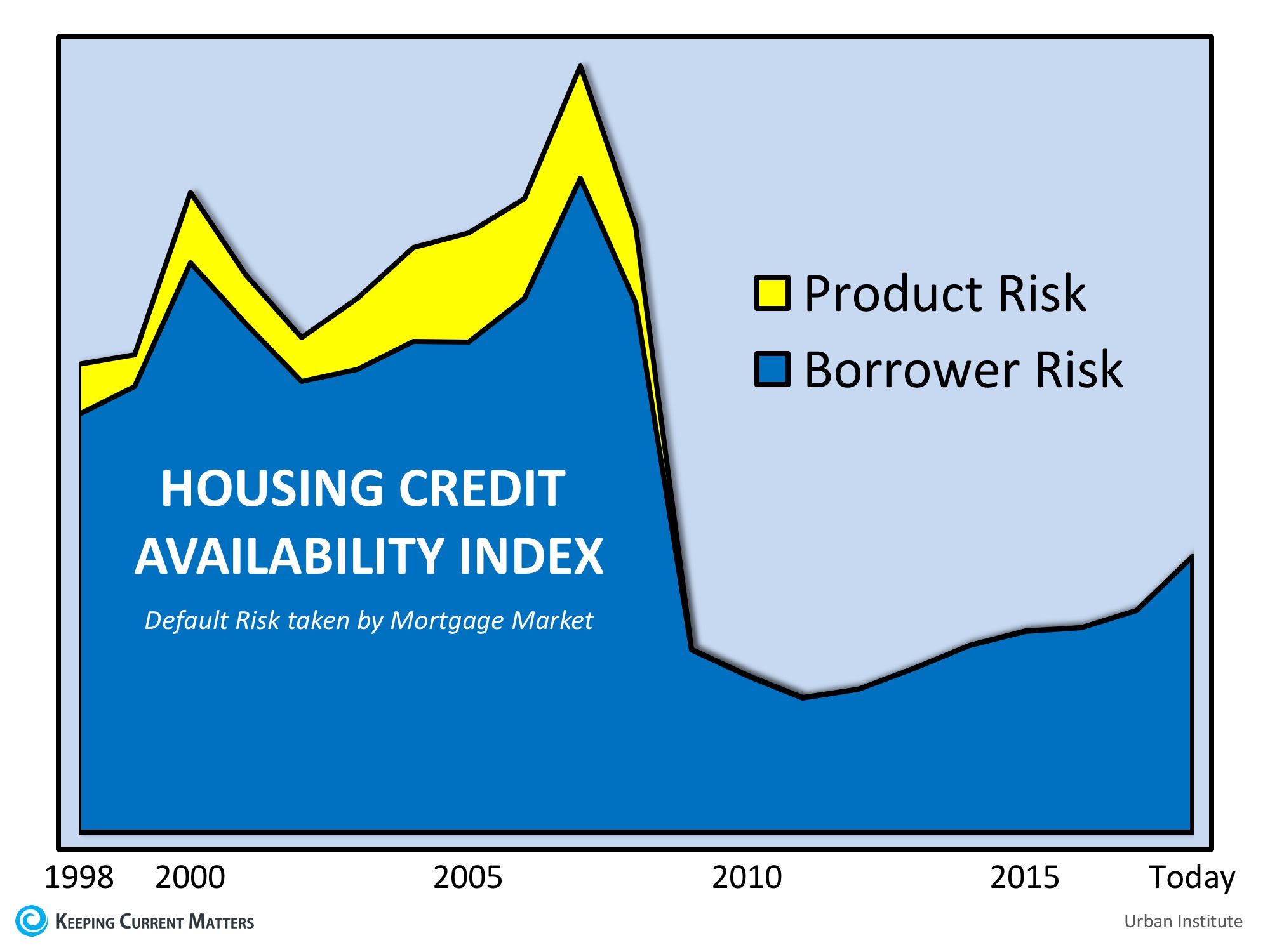
The Urban Institute’s Housing Finance Policy Center issues a monthly index which measures the percentage of home purchase loans that are likely to default. A lower score indicates that lenders are unwilling to tolerate defaults and are imposing tighter lending standards. A higher score indicates that lenders are willing to tolerate defaults and are taking more risks.
Their July Housing Credit Availability Index revealed credit availability rose to 5.9%. For context, they went on to explain:
“Significant space remains to safely expand the credit box. If the current default risk was doubled across all channels, risk would still be well within the pre-crisis standard of 12.5 percent from 2001 to 2003 for the whole mortgage market.”
Here is a graph depicting the Urban Institute’s findings:
Bottom Line
Though it may be slightly easier to get a mortgage today than it was a year ago, lending standards are nowhere near where they were during the build-up to the housing bubble.
- How AI Virtual Staging Helps Homes Sell Faster (Without Expensive Renovations)
- The Most Effective Way to Build Wealth Using Real Estate (That Most People Overlook)
- Accept, Counter, or Reject: Navigating Your Home Sale Offer
- Why Tennessee Was the Top Choice for Moving States: Top Four Reasons Revealed!
- Pros and Cons of Living in Murfreesboro, Tennessee (Complete Guide)